|
|
| 学会・論文発表 |
 |
A.D. Semyonov, A.V.Doga, G.F.Kachalina,
K.Okuyama, I.A.Alisov, N.A.Semyonova
Specific Features of Clinical Course in Photoastigmatic Refractive
Keratectomy with the "Profil-500"at Different Terms Postoperatively
|
|
Numerous studies investigating the condition of the cornea at different terms
after photorefractive keratectomy(PRK) and photoastigmatic refractive
Keratectomy(PARK) indicate tnat tne corneal syndrome is the typical feature of
clinical course in the early postoperative period of these excimerlaser
interventions in myopia and myopic astigmatism. The degree of syn drome
indetermined by the type and area of erosion surface,time and period of cornea
epithelialization,and condition of corneal epithelium anu stroma by the moment
of completing epithelialization. Many authors consider the above facts to play
an important role in the further development of subepithelial fibroplasia which
forms corneal opacities of different degrree leading to unpredictable regression
of postoperative refractive result[1,3,6,9,12,13]
Notably, from
literature, the techniques of PRK and PARK with different foreign excimer laser
devices are performed with preliminary scarification of the corneal epithelium
[4,5,7,8]. Thus, it's necessary to stress that the device "Profil-500"
elaborated at the Center of Laser Surgery of the Eye Microsurgery Complex, like
all previous Profil models of several generations ,allows transepithelial
correction of myopia and myopic astigmatism i.e., without preliminary
scarification of epithelium.
The objective of the work is to study clinical
course of the postoperative period after transepithelial PARK with "Profil-500"
on the basis of postoperative results.
Material and methods
PARK was performed in 250 eye sof 131 patients aged 18 to 45 years with
compound myopic astigmatism to 5.OD with myopia to 1O.OD. The follow−up was 3
years.
In all cases the operation was performed by transepithelial method,
i.e., with subsequent evaporation of epithelium, Bowman's membrane and
superficial layers of the corneal stroma. The operation lasted not more than 1.5
min. No intraoperative complications were recorded.
Biomicroscopy of the
anterior sector in eyes operated on was performed
using slit-lamp("opton”,Germany). To evaluate tne pattern and duration of
corneal epithelialization and find defects in it, we used fluorescein probe
according to routine method with the
use of 1% fluorescein solution.
We
evaluated in the postoperative period(a) the degree of corneal syndrome and
subepithelial fibroplasia according to the classification developed at the Eye
microsurgery Complex(Kornilovsky I.M.,1995) [2]; (b) degree of corneal opacities
according to the world numeric classification accepted in excimer laser
practice.
Results and discussion
In most eyes operated on (184eyes-73.6%),irrespective of the degree of
initial astigmatism and sphere equivalent(SE),We found epithelial form
of corneal syndrome manifested by minimal involvement of corneal stromal
layers adjacent to ablation zone. In these cases ablation zone was completely
covered with epithelium within 24−36h postoperatively; edema of superficial
corneal stromal layeres adjacent to intervention zone was rather mild or
almost absent. Photophobia and lacrimation disappeared 1-2 days postoperatively
as a rule. In 66 eyes(26.4%) stromal type of the corneal syndrome was recorded
which was accompanied by moderate edema of all stromal layers in ablation
zone. Notablv, in these eves the initial SE varied from 8.25 to 15.0 D,
being more than 10.0 D on average. This required the removal of great volume
of tissue and, thus, the use of greater energy and pulse number for photochemical
evaporation of the cornea. Complete epithelialization in these eyes was
recorded 36-48 h postoperatively; stromal edema gradually decreased with
epithelialization and almost disappeared by day 5-7 postoperatively. Notably,
we found no cases of mixed type of the corneal syndrome consisting in longer
epithelialization to 72 and more hours postoperatively and pronounced stromal
edema of entire ablation zone with signs of descemetitis. This was confirmed
by fluorescein probe allowing detailed evaluation of corneal epithelialization
and exclusion of uneven and chaotic epithelialization with poorly fixed
and mobile epithelium. Thus, uncomplicated postoperative course after transepithelial
PARK was recorded in almost all cases By day 5-7 postoperatively the anterior
eye sector was calm, the cornea was smooth, bright and transparent. Only
in some cases biomicroscopy revealed slightly thickened epithelial layer
of the cornea with mild subep ithelial opalescence; its intensification
accompanied by appearance of whitish inclusions in the cornea are considered
to be the first signs of development of subep ithelial fibroplasia [2].
We analyzed clinical course of transepithelial PARK at different terms
of postoperative period and recorded no visible signs of fibroplasia(degree
0) in 136(54.4%) eyes from the first days after surgery and during the
whole follow-up to 3 years. As a rule, SE in these cases did not exceed
8.5 D. In 92(36.8%)eyes 8-14 days postpperatively and irrespective of the
value of initial refraction, reversible form of subepithelial fibroplasia
was recorded. Its symptoms intensified during 1-3 months postoperatively
and gradually disappeared by 6-12 months postoperatvely. From our viewpoint,
timely and correct topical corticosteroid and resolving therapy affected
the rate of fibroplasia regression that in agreement with data of other
authors[10, 11] Partially reversible type of fibroplasia was recorded in
22(8.8%) eyes. Average SE was higher tnan 10.0 D ln these eyes. Due to
medication (corticosteroid and resolving therapy) only delicate and spotty
opacities of 0.5-1 degree remained at tne periphery and in tne center of
ablation zone by 6-l2 months after PARK which almost did not affect postoperative
visual acuity and did not cause its decrease as compared tothatwithglassespreoperatively.
|
We found irreversible subepithelial fibroplasia with signs of pronounced
fibrosis in the corneal stroma and accompanied by significant decrease of
refractive effect in none of the cases. This data correlate with results of
clinical observations at the Center of Laser Surgery of Eye Microsurgery Complex
analyzing 40,000 PRK and indicating that this type of fibroplasia is rather rare
and its occurrence is not more than 1.4% of cases. The degree of manifestation
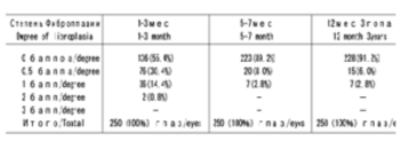
of postoperative corneal opacities in ablation zone is presented in Table.
Thus, 6-12 months after PARK and during the further follow-up until 3 years
corneal opacities caused by subePithelial fibroplasia were recorded in only 8.8%
of cases. Transepithelial access in PARK technique using "Profil-500" allows
significant degrease of degree and duration of corneal syndrome and decreases
1.5-2 times the period of complete epithelialization of the cornea that, in
turn, sharply reduces the degree of subepithelial fibroplasia in postoperative
period and significantly increases the percentage of high and stable refractive
results |
|
|
| レーシック、レーシック・フラップレス等近視矯正手術の最新情報をお届けする近視手術友の会のホームページ |
|
|