情報化された現代社会に生きる私たちの目は、仕事や勉強、生活環境によって疲れきっています。
まずは疲れを癒して、視力回復を目指しましょう!
2003年8月18日 発行
著者 THREE DEMENSYON LABORATORY
監修 奥山公道 定価 本体 933円+税
発行 コスミック出版 / 発売 コスミックインターナショナル
この本を購入→
2005年3月31日
みるみる目がよくなるアイマジック
アイ・マジック

眼力を鍛える!
仕事や勉強の合間に眼をリフレッシュ!
疲れ眼・かすみ眼は、酷使されている眼からの危険信号!
著者 立体アート研究所
監修 奥山公道 定価 本体 648円+税
発行 株式会社 コスミック出版
2004年10月11日
視界開け「バラ色人生」
2004年(平成16年)10月11日 毎日新聞より抜粋
病院がわかる 視界開け「バラ色人生」
近視の矯正手術を受けた後の世界は、明るく美しかった。東京都内の会社役員、晴子さん(44)=仮名=は「葉っぱひとつ見ても、複雑な色合いに感激した。人生そのものがバラ色に思えました」と振り返る。
小学生の頃から強い近視に悩んでいた。裸眼で0.01の視力は、コンタクトレンズで矯正しても0.8.木の葉は、のっぺりした緑一色にしか見えなかった。昨年10月に手術し、現在の視力は1.5.それまで全く経験していない視力を得た感激は大きい。
晴子さんが受けた手術は「LASIK(レーシック)」と呼ばれる。角膜表面の一部を薄くスライスし、熱による変性をほとんど起こさないエキシマレーザーで角膜の実質を削り、近視や乱視を治す。角膜表面を削らないため、痛みや炎症が少なく、視力の回復が早いのが特長だ。費用は両眼で50~60万円かかる。
国内のコンタクトレンズ装用者は約1500万人。パソコンを使う職場の増加もあり、近視者は増える一方だ。LASIKのほか、アルコールで角膜表面をはがしてレーザー光を照射する「LASEK(ラセック)」、睡眠時に特殊なコンタクトレンズを装着して角膜の形を矯正する「オルソケラトロジー」などいくつもの矯正方法が開発されている。
2003年12月11日
Wave-front and Fourier Analysis of the High Myopia Transepithelial PRK on Profile-500
 Wave-front and Fourier Analysis of the High Myopia Transepithelial PRK on Profile-500
Wave-front and Fourier Analysis of the High Myopia Transepithelial PRK on Profile-500
Author(s):Kodo Okuyama,Viktor Movshev
Hospital or Institution:Sangubashi Eye Clinic,IRTC Microsurgery
Address for Correspondence: 1-2-15-201 Higashigotanda Shinagawa-ku Tokyo JAPAN
Tel : 81+3+34463902Fax : 81+3+3782178
Email:okuyama@k.email.ne.jp
Purpose: To evaluate the predictability, safety, and long term stability of transepithelial PRK for the correction of the high and very high myopia and astigmatism using the Profile-500 Gaussian beam excimer laser.
Methods: We choose at random 10 patients,18 eyes,with high(8 eyes)and very high myopia(10eyes).Among the 7 females and 3 males.Mean age was37.7 years. Before the transepithelial PRK there was routine refractive examinations,contrast sensitivity and endothelial cell counts. After the operation we tried to evaluate the operation,using by KR-9000 PW Wavefront analyzer and TMS-2N videokeratotopograph.
Results:Mean Spherical Equivalent before the operation was -11.5+/-0.38D,after the operation was -1.75+/-0.42D. Three eyes were operated twice due to haze classified as Fantes 1 to 2. Wavefront analyzer and Fourier Analysis show the appearance of prismatic effect. There is not significant high order irregularity. After the second operation all three eyes decrease haze level to Fantes 0.5.
Conclusion : Ablation patterns of the Gaussian beam at a given fluence level of the Profile-500 gives us aspherical surfaces with optimal balance between defocusing and spherical aberration for patient with high myopia. We can not see significant reduction of contrast sensitivity. In some case with haze for 3 to 12 months contrast sensitivity reduced, however after disappearing of haze the contrast sensitivity returned to the previous level.
Biochemical Investigations of Lacrima in Early Diagnosis of Keratoconus
Author(s): Leonid Legkikh1, M. Koledintsev2, A. Semenova2, K.Okuyama3
Hospital or Institution: 1. Svyatoslav Fyodorov S.I. Eye Microsurgery complex, Beskudnikovsky Blvd.59A 127486, Moscow, Russia Moscow, Russia
2. Moscow Medical Stomatological University, Moscow, Russia
3.Sangubashi Eye Clinic, Tokyo, Japan
Purpose: To study results of biochemical investigation of lacrimal fluid in patients with initial keratoconus to develop tests of early diagnosis of disease.
Methods: 26 patients with initial keratoconus aged from 16 to 44 years were examined The control group consists of 20 practically healthy people in the same age. The biochemical investigation of lacrima was performed with the biochemical analyzer.
Results : The biochemical analysis of lacrima showed, that an increase of activation of Lactate dehydrogenase, creatine phosphokinase, amylase etc. These data in combination with an increase of general protein and products of albuminolysis(urea, uric acid) compared with the control group is notable for patients with initial keratoconus.
Conclusion: The method of biochemical analysis of lacrimal fluid can be used in the early diagnosis of keratoconus.
Immunologic Investigations of Lacrima in early Diagnosis Keratoconus
Author(s): Anna Semenova 1, M. Koledintsev 2, L. Legkikh 1, K. Okuyama 3
Hospital or Institution: Svyatoslav Fyodorov S.I.”Eye Microsurgery Complex
Address for Correspondence: Beskudnikovsky Blvd. 59A, 127486, Moscow, Russia
E-mail :semenaru @yahoo.com
Tel: (095) 488-8424 Fax: (095) 905-5333
Purpose: To study results of immunologic investigations of lacrima in patients with initialkeratoconus for development of tests of early diagnosis of disease
Setting/Venue:1.Svyatoslav Fyodorov S.I. Eye Microsurgery Complex,Moscow,Russia
2.Moscow Medical Stomatological University.
3.Sangubashi Eye Clinic,Tokyo,Japan.
Methods: 26 patients with initial keratoconus aged from 16 to 44 years were examined. The Control group consists of 20 practically healthy people of the same age. The immunologic investigation of lacrima included a determination of concentration of A,M,G immunoglobulins by method of Manchini G.Radial immunodiffusion.
Results: The immunologic investigation of lacrima showed a significant Ig A increase in18 of 26 patients(69.2%). A significant increase Ig G in 53.8%.
We noted a tendency to increase of Ig M compared with the control. The difference was not significant. Thus, considerable differences in the level of immune proteins of lacrima were noted in patients with keratoconus compared with the control..
Conclusions: Methods of immunologic investigation of lacrima can be used in the early diagnosis of keratoconus.
2003年8月20日
Induction of the heat shock protein in rat lungs following intermittent hypoxic training
Induction of the heat shock protein in rat lungs following intermittent hypoxic training
KoDo Okuyama 1), Jingtao Jiang 2)
Clinical Research Laboratory of ‘Mountain Air’ Therapy 2-21-15 Shimouma Setagaya-ku Tokyo JAPAN
Central Institute for Electron Microscopic Researches, Nippon Medical School, Sendagi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan.
Abstract
In order to demonstrate the mechanism of intermittent hypoxic training (IHT), we studied the expression of HSP70 by immunohistochemistry using the Streptavidin Biotin Peroxidase Complex(SABC) Method on alveolar type I , type II epithelial cells, macrophages from rats with IHT. The expression of HSP70 in IHT in comparison with control was significantly increased on alveolar type I , type II epithelial cells, macrophages and was significantly correlated with the duration of IHT.
This study demonstrates that expression of HSP70 may be a mechanism of adaptation of hypoxia by IHT.
Key words: Intermittent hypoxic training HSP70 Electron microcopy Immunohistochemistry
lntroduction
Intermittent hypoxic training (IHT), with repeated short-term inhalation of hypoxic mixtures, has been used to treat and prevent certain diseases and has a very favorable effect for the exercise of athletes 1,2. Investigations of IHT have showed that increased hypoxic ventilatory response (HVR) 3,4 is an important physiological response. Resent studies have displayed that IHT inhibits the free radical production, which gives harmful effect to the cells and tissues, and raise the metabolic rate as a result of sympathetic nervous system activation 5,6. Rats trained to intermittent normobaric hypoxia developed an increase of the glycogen contents in the heart and liver parenchymatous cells and offered as many beneficial effects in protecting against myocardial injuries 7,8. Antixidant enzymes and stress proteins may be part of the mechanisms contributing to the cardioprotection of the intermittent hypoxic adaptation 7.Heat shock causes intracellular expression of a specific group of proteins called heat steins (HSPs) that have broad cytoprotective properties 9,10. The first demonstration of HSP- mediated cytoprotection involved the phenomenon of thermotolerance, whereby a brief heat shock conferred protectionagainst subsequent exposure to otherwise lethal hyperthermia 11. Subsequent studies demonstrated that induction of HSPs also protected cells and whole organs against nonthermal cytotoxic agents such as oxidants, nitric oxide, tumor necrosis factor-α, and endotoxin 12-14. Previous studies also demonstrated that induction of HSPs protected against in vitro and in vivo models of acute lung injury and may have therapeutic value for attenuating acute lung injury . HSP 70 has been shown to be protective following ischemic injury. Similarly, a member of the small heat shock family, HSP27 has been shown to play a role in cellular repair and mechanisms of protection against cell stress. In this study, we are used monoclonal antibody to heat shock protein 70 to investigate whether IHT induces the expression of HSP70 in lungs.
Materials and methods
1. Animals
A total of 18 male Wistar rats, aged 12 weeks were used: three animals for control and rest for the experimental groups. They were allowed free access to food and water during intermittent hypoxic training.
2.Intermittent hypoxic training:
Hypoxia was induced by exposure to 10% oxygen with machine. The rats were sustained hypoxia for 15min one time a day for 3, 7, or 21 consecutive days, respectively. Control rats exposured toroom air.
3. Light and electron microscopy.
At 3D, 7D and 21 Days after intermittent hypoxic training (IHT), the animals were anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium (50mg/kg) and lungs were removed. For light microscopic examination, the tissues were fixed with 10% formalin in phosphate buffer solution, and embedded in paraffin.
Then paraffin sections of 2 μm in thickness were prepared and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. For electron microscopic examination, rat lung specimens were cut into 2mm3 blocks, fixed 2.5% glutaraldehyde in 0.1M phosphate buffer and
postfixed with 1% osmium tetroxide, dehydrated in a graded alcohol series and embedded in Epon 812. Semithin sections stained with toluidine blue were used for high light microscopy and selection of areas for thin sectioning. Thin sections were cut with 5000 Ultrotome, stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate. The sections were examined under a JEM- 1010 transmission electron microscope.
4. Immunohistochemistry
The Streptavidin Biotin Peroxidase Complex (SABC) Method was employed for immunohistochemistry for heat shock protein (HSF70). Briefly, deparaffinized sections were treated for 30 min with 0.3% H2O2 to block endogenous peroxidase and rinsed again 3×5 min inPBS. Sections were then incubated for 30 min with block nonspecific reactive sites by applying 1 :20 normal goat serum and incubated with Monoclonal anti-HSP antibody (NOVO) diluted 1:40 in PBS for 60 min. After washing in PBS, they were incubated with goat anti-mouse immunoglobulins for 10 min and then incubated with a mixture of streptavidin and biotinylated horseradish peroxidase for 5 min. After washing in PBS, reacted with 0.05% 3 – 3′ diaminobenzidine (DAB) containing 0.01 %H2O2.
Results
Light microscopic observations
The morphological observations in the control group were normal from 3 days to 21 days. After three days IHT, the remarkable interstitial edema,increased thickness of the alveolar septa, marked capillary dilatation,proliferation of interstitial cells, the collapse of alveoli and dilation of the alveolar ducts were observed compared with controls (Fig. 1A). After 7 days IHT, those pathologic changes decreased than 3 days (Fig.1B). After 21 days of IHT, the nearly normal structure of lungs was observed (Fig.1C).
Immunohistochemical observation
The heat shock protein 70 monoclonal antibody was used to stain the lung tissue from the control and IHT rats immunohistochemically. In control lungs, there are weak positive staining for HSP70 observed in the bronchial epithelial cells as well as in some alveolar type II epithelial cells.
After 3 days IHT, HSP70 was moderately expressed in alveolar type I ,type II epithelial cells, macrophages and bronchial epithelial cells. HSP70 expressed in cytoplasm and nuclei (Fig.2A). After 7 days IHT, expression of HSP70 was same as 3 days IHT (Fig.2B). After 21 days IHT, there was strong septa also were displayed. By 7 days, the congestion of capillary, type II cell proliferation, and lipid drops in alveolar septa were observed. By 21 days,congestion of capillary, increased capillaryendothelial volume, lipid drops in the alveolar septa and proliferation of alveolar type II cells were noted(Fig.3B).
Discussion :
The principle of intermittent hypoxic training (IHT), with repeated short-term inhalation of hypoxic mixtures had been proposed by S. Strelkov and his associates in the early of 1980’s based on their obstetrical practice. Intermittent hypoxic training (IHT) has showed promise for prevention and treatment of some diseases and efficiently produces great advancement in athletic training 1,2. The mechanism of IHT remains unidentified. A number of mechanisms have been postulated including optimizing both hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis functioning and free radical-mediated process control 5, increase of the quantity and secretory activity of peptidergic neurons of the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus (PHN) 16,enhancement of neurotransmission in the carotid body (CB) as well as in central
structures through NADPH oxidase stimulation 17, increase in ventilatory response under repetitive hypoxia, changes in suprapontine facilitation of resporatory activity and Changes in monoamine metabolism or release 18, and raise the metabolic rate as a result of sympathetic nervous system activation 6.
In our clinical practice, we found that IHT could release the stress in some patients. In this study, we found that IHT induced the expression of HSP70. The response of cells or organisms to stress such as exposure to heat or chemicals is associated with the induction of heat shock proteins (HSPs). Heat shock proteins (HSPs) are an evolutionarily conserved group of proteins that are highly inducible by a wide variety of stressors. HSPs are grouped by molecular weight and amino acid sequence similarity into five main families: The high molecular weight 100-110kDa family; the 83-90kDa family; the 70kDa family ranging from 66 to 78kDa and containing the highly inducible HSP 70; the 60kDa family present in bacteria,mitochondria, and chloroplasts; and a diverse group of small HSPs ranging from 15 to 30kDa. Of great interest are observations demonstrating that once a heat shock response has been induced, the cells or organs can show remarkable resistance to subsequent metabolic stress. Heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) has been shown to have a protective role in ischemic disease,inflammation, infection and a potential role in antigen processing as well as a possible regulatory role in cytokine biosythesis 13,14. HSP70 exists in the cell in equilibrium between its free state, in the cytoplasm, and its bound state, protecting proteins in the nucleolus, perhaps either by helping refold some of the unfolded ribosomal proteins or by solubilising the denatured ribosomal proteins to facilitate their turnover. During release from heat shock and as the nucleoli begin to recover their normal activities, most of the HSP 70 returns to the cytoplasm. Stress proteins have an important role in normal cellular physiology apart from participation in the stress response. Under normal conditions, stress proteins are involved in the successful folding, assembly, intracellular localization, and secretion of nascent protein chains as they emerge from the ribosome. Stress proteins also function to regulate the degradation of proteins to prevent the accumulation of protein aggregates within the cell. Cultured bovien and ovine pulmonory artery endothelial cells and guinea pig airway epithelial cells and alveolary macrophages expressed abundant HSP 70 after thermal stress14, 19, 20. In rabbit alveolar type II cells, the process of cell isolation itself induced stress protein expression 21. In vivo thermal stress increased stress protein expression in the lungs and other organs of rats, and the time courses and relative magnitudes of expression differed among organs 22,23. Bonay et al demonstrated limited stress protein expression in normal human lungs. HSP90, HSP 70 and HSP63 were selectively expressed in proximal bronchiolar epithelium and alveolar macrophage. In contrast, more distal bronchiolar epithelium, type I and type II alveolar cells, and stromal cells did not express stress proteins 24. HSP 70 expression was substantially increased in airway epithelium and alveolar macrophages of patients with asthma compared with control subjects 25. In this study, we observed the morphologic changes of lungs and expression of HSP70 after rat IHT. We found that that pulmonary damage occurred at 3 days IHT, one week IHT later, the pulmonary damage repaired in hypoxic animals. The expression of HSP70 observed in alveolar type I, type IIepithelial cells,macrophages and bronchial epithelial cells after 3 dr 3 days IHT, andcontinually expressed until 2l days IHT. Expression of HSP 70 in 21 days IHT was stronger than 3 days IHT. This revealed that IHT could induce HSP70 in alveolar type I , type II epithelial cells, macrophages and bronchial epithelial cellsveolar type I, type II epithelial cells, macrophages and bronchial epithelial cells after IHT. HSP70 expressed after 3 days IHT, and continued to 21 days IHT. Although the exact significance of these data is still unresolved, it is proposed expression of HSP may be a mechanism of adaptation of hypoxia with IHT.
Reference
1 Serebrovskaya T, Swanson R, Karaban IN, Serebrovskaya Z, Kolesnikova EE. Intermittent hypoxia alters hypoxic ventilatory responses. Fiziol Zh. 45(5): 9-18, l999
2 Serebrovskaya T, Swarotective effect of stress protein induction in a rat model of acute lung injury caused by intratracheal administration of phospholipase A1 and systemic administration of endotoxin 22,23.This study is the first to demonstrate an expression of HSP 70 in abbins PA.Alterations in respiratory control during 8 h of isocapnic and poikilocapnic hypoxia in humans. J Appl Physiol. 78: 1098-107,1995
4 Schoene RB, Roach RC, Hackett PH, Sutton JR, Cymerman A, Houston CS, Operation Everest II: ventilatory adaptation during gradual decompression to extreme altitude. Med Sci Sports & Exercise. 22:804- 10,1990
5 Adiiatulin AI, Piliavskaia AN, Takchuk EN, Guliaeva NV, [Various mechanisms of protective action of interval hypoxic training during preparation for abdominal dapy. Adaptation Biology and Medicine(Vol.3).
6 Cao KY, Zwillich CW, Berthon-Jones M, Sullivan CE. Increased normoxic ventilation induced by repetitive hypoxia inconscious dogs. J Appl Physiol. 73:2083.8, l992
7. Zhuang J, Zhou Z. Protective effects of intermittent hypoxic adaptation on
myocardium and its mechanisms. Biol Sinals Recept. 8:316-22,1999.Review.
8. Lebkova NP, Chizhov AI, Bobkov II. The adaptational intracellular mechanism regulating energy homeostasis during intermittent normobaric hypoxia. Ross Fiziol Zh lm I M Sechenova. 85:403-11, 1999
9. Minowada G, Welch WJ: Clinical implications of the stress response. J Clin. Invest. 95:3-12, 1995
10. Wang HR, Eispe JR: The stress response and the lung. Am J Physiol 273: L1-9, l997
11. Gerner EW, Schneider MJ: Induced thermal resistance in Hela cells. Nature 256:500-2, 1975
12. Meerson FZ, Malyshev I Yu, Zamotrinsky AV. Differences in adaptive stabilization of structures in response to stress and hypoxia relate with the accumulation of hsp 70 isoforms. Mol Cell Biochem. 111:87-95, 1992
13. Koh Y, Lim CM, Kim MJ, Shin TS, Lee SD, Kim WS, Kim DS, Kim WD. Heat shock response decrease endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rats. Respirology.4:325-30, 1999
14. Wong HR, R.J Mannix, J.M. Rusnak, A. Boota, H. Zar, S. C. Watkins, J.S. Lazo,B.R. Pitt. The heat shock response attenuates lipopolysaccharide-mediated apoptosis in cultured sheep pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. :745-51, 1996
15. Wong HR, Ryan M, Menedez IY, Denenberg A and Wispe JRlar hypothalamic nucleus and brain stem neurons in rats]. [Russian] Ross Fiziol Zh lm I. M. Sechenova. 84(3): 173-81, 1998
17 0lano M, Song D, Murphy S, Wilson DF, Pastuszko A. Relationships of dopamine, cortical oxygen pressure, and hydroxyl radicals in brain of newborn piglets during hypoxia and posthypoxic recovery. J Neurochem. 65(3):1205-12, 1995
18. Soto-Arape I, Burton MD, Kazemi H. Central amino acid neurotransmitters and the hypoxic ventilatory response. American J Respir Crit Care Med. 151(4):1113-20, 1995
19. Rinaldo J. E, M. Gorry R, Stricter H, Cowan R, Abdolrasulnia V. Shepard. Effect of endotoxin-induced cell injury on 70-kD heat shock proteins in bovine lung endothelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 3:207-16, 1990
20. Cohen D.S, E. Palmer WJ, Welch, D. Sheppard. The respose of guinea pig airway epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages to environmental stress. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 5:133-43, 1991
21. Brandes M. E, J. N Finkelstein. Induction of the stress response by isolation of rabbit type II pneumocytes. Exp. Lung.Res. 15: 93-111, 1989.
22. Villar J, J. D. Edelson, M. Post, B. Mullen, A. S. Slutsky. Induction of heat Stress proteins is associated with decreased mortality in an animal model of acute lung injury. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. l47:177-81, l993.
23. Villar J.,S.P.Ribeiro,J.B.M.Mullen,M.Kuliszewski,M.Post,A.S.Slutsky.Induction of the heat shock response reduces mortality rate and organ damage in a sepsis-induced acute lung injury model. Crit. Care Med. 22:9 B ± through preventing I o B kinase activation in 0respiratory epithelial cells. J. Immunol 164:541 6-23, 2000
27. Yoo, C.G., Lee S., Lee C. T., Rim Y. W., Ham S. K., and Shin Y. S. Anti-inflammatory effect of heat shock protein induction is related to stabilization of I κ B α through preventing I κ B kinase activation in respiratory epithelial cells. J. Immunol 164:5416-23, 2000
28. Simon M. M, A. Reikerstolfer, A. Schwarz, C. Kronis, T. G.Lunger, M. Jaatela, T. Schwarz. Heat shock protein 70 overexpression affects the response to ultraviolet light in murine fibroblast. J. Clin. Invest. 95:926-933,1995
Figure Legends
Fig 1 Change of light microscope in IHT rat lungs. A: 3 days IHT. B:7days IHT.
C: 21 days IHT.
Fig 2 Immunohistochemical staining of rat lung with anti-HSP70 after IHT.
A: 3 days IHT. B: 7 days IHT. C: 21 days IHT.
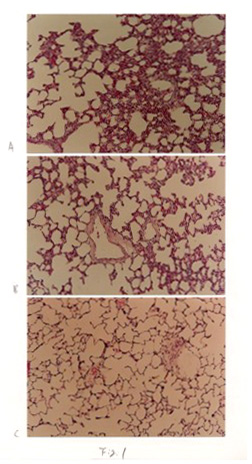
Fig 3 Ultrastructural changes of lung in IHT: A: 3 days IHT. B: 21 days IHT
2001年7月2日
Ophthalmosurgery
 A.D. Semyonov, A.V.Doga, G.F.Kachalina,
A.D. Semyonov, A.V.Doga, G.F.Kachalina,
K.Okuyama, I.A.Alisov, N.A.Semyonova
Specific Features of Clinical Course in Photoastigmatic Refractive Keratectomy with the “Profil-500″at Different Terms Postoperatively
The work analyzes the clinical course of PARK performed using the “Profil-500″ in 250 eyes with compound myopic astigmatism to 5.0D with myopia to 10.0D. Operation was done through transepithelial access. ln all cases complete epithelialization of the cornea was recorded within 24-48h. By 6-12 months postoperatively and until 3years of follow-up the cornea of eyes operated on was comPletely transparent in 91.2% of cases; opacities of 0.5-1 degree Were found in 8.8% of cases which did not affect final refractive result.
Numerous studies investigating the condition of the cornea at different terms after photorefractive keratectomy(PRK) and photoastigmatic refractive Keratectomy(PARK) indicate tnat tne corneal syndrome is the typical feature of clinical course in the early postoperative period of these excimerlaser interventions in myopia and myopic astigmatism. The degree of syn drome indetermined by the type and area of erosion surface,time and period of cornea epithelialization,and condition of corneal epithelium anu stroma by the moment of completing epithelialization. Many authors consider the above facts to play an important role in the further development of subepithelial fibroplasia which forms corneal opacities of different degrree leading to unpredictable regression of postoperative refractive result[1,3,6,9,12,13]
Notably, from literature, the techniques of PRK and PARK with different foreign excimer laser devices are performed with preliminary scarification of the corneal epithelium [4,5,7,8]. Thus, it’s necessary to stress that the device “Profil-500″ elaborated at the Center of Laser Surgery of the Eye Microsurgery Complex, like all previous Profil models of several generations ,allows transepithelial correction of myopia and myopic astigmatism i.e., without preliminary scarification of epithelium.
The objective of the work is to study clinical course of the postoperative period after transepithelial PARK with “Profil-500″ on the basis of postoperative results.
Material and methods
PARK was performed in 250 eye sof 131 patients aged 18 to 45 years with compound myopic astigmatism to 5.OD with myopia to 1O.OD. The follow-up was 3 years.
In all cases the operation was performed by transepithelial method, i.e., with subsequent evaporation of epithelium, Bowman’s membrane and superficial layers of the corneal stroma. The operation lasted not more than 1.5 min. No intraoperative complications were recorded.
Biomicroscopy of the anterior sector in eyes operated on was performed using slit-lamp(“opton”,Germany). To evaluate tne pattern and duration of corneal epithelialization and find defects in it, we used fluorescein probe according to routine method with the
use of 1% fluorescein solution.
We evaluated in the postoperative period(a) the degree of corneal syndrome and subepithelial fibroplasia according to the classification developed at the Eye microsurgery Complex(Kornilovsky I.M.,1995) [2]; (b) degree of corneal opacities according to the world numeric classification accepted in excimer laser practice.
Results and discussion
In most eyes operated on (184eyes-73.6%),irrespective of the degree of initial astigmatism and sphere equivalent(SE),We found epithelial form of corneal syndrome manifested by minimal involvement of corneal stromal layers adjacent to ablation zone. In these cases ablation zone was completely covered with epithelium within 24-36h postoperatively; edema of superficial corneal stromal layeres adjacent to intervention zone was rather mild or almost absent. Photophobia and lacrimation disappeared 1-2 days postoperatively as a rule. In 66 eyes(26.4%) stromal type of the corneal syndrome was recorded which was accompanied by moderate edema of all stromal layers in ablation zone. Notablv, in these eves the initial SE varied from 8.25 to 15.0 D, being more than 10.0 D on average. This required the removal of great volume of tissue and, thus, the use of greater energy and pulse number for photochemical evaporation of the cornea. Complete epithelialization in these eyes was recorded 36-48 h postoperatively; stromal edema gradually decreased with epithelialization and almost disappeared by day 5-7 postoperatively. Notably, we found no cases of mixed type of the corneal syndrome consisting in longer epithelialization to 72 and more hours postoperatively and pronounced stromal edema of entire ablation zone with signs of descemetitis. This was confirmed by fluorescein probe allowing detailed evaluation of corneal epithelialization and exclusion of uneven and chaotic epithelialization with poorly fixed and mobile epithelium. Thus, uncomplicated postoperative course after transepithelial PARK was recorded in almost all cases By day 5-7 postoperatively the anterior eye sector was calm, the cornea was smooth, bright and transparent. Only in some cases biomicroscopy revealed slightly thickened epithelial layer of the cornea with mild subep ithelial opalescence; its intensification accompanied by appearance of whitish inclusions in the cornea are considered to be the first signs of development of subep ithelial fibroplasia [2]. We analyzed clinical course of transepithelial PARK at different terms of postoperative period and recorded no visible signs of fibroplasia(degree 0) in 136(54.4%) eyes from the first days after surgery and during the whole follow-up to 3 years. As a rule, SE in these cases did not exceed 8.5 D. In 92(36.8%)eyes 8-14 days postpperatively and irrespective of the value of initial refraction, reversible form of subepithelial fibroplasia was recorded. Its symptoms intensified during 1-3 months postoperatively and gradually disappeared by 6-12 months postoperatvely. From our viewpoint, timely and correct topical corticosteroid and resolving therapy affected the rate of fibroplasia regression that in agreement with data of other authors[10, 11] Partially reversible type of fibroplasia was recorded in 22(8.8%) eyes. Average SE was higher tnan 10.0 D ln these eyes. Due to medication (corticosteroid and resolving therapy) only delicate and spotty opacities of 0.5-1 degree remained at tne periphery and in tne center of ablation zone by 6-l2 months after PARK which almost did not affect postoperative visual acuity and did not cause its decrease as compared to that with glasses preoperatively.
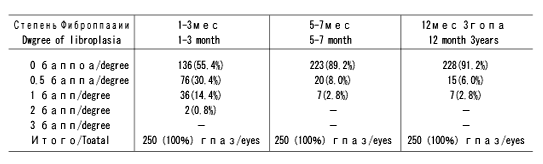
We found irreversible subepithelial fibroplasia with signs of pronounced fibrosis in the corneal stroma and accompanied by significant decrease of refractive effect in none of the cases. This data correlate with results of clinical observations at the Center of Laser Surgery of Eye Microsurgery Complex analyzing 40,000 PRK and indicating that this type of fibroplasia is rather rare and its occurrence is not more than 1.4% of cases. The degree of manifestation of postoperative corneal opacities in ablation zone is presented in Table.
Thus, 6-12 months after PARK and during the further follow-up until 3 years corneal opacities caused by subePithelial fibroplasia were recorded in only 8.8% of cases. Transepithelial access in PARK technique using “Profil-500″ allows significant degrease of degree and duration of corneal syndrome and decreases 1.5-2 times the period of complete epithelialization of the cornea that, in turn, sharply reduces the degree of subepithelial fibroplasia in postoperative period and significantly increases the percentage of high and stable refractive results.
2001年5月3日
2001年度分(メディア掲載)
| 日付 | 雑誌・新聞名 | 会社 | ページ | 執筆 | 内容 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.1 | 月刊FLIX | ビジネス社 | 109 | 奥山 | 目と映画 |
| 12. 1 | 月刊 現代 | 講談社 | 160 | 奥山 | 歯・眼・腰 3大慢性病の最新治療法 近視の視力回復はここまで進んだ。 |
| 10.10 | ミスター・パートナー No157 | 125 | 奥山 | 近視矯正手術で眼鏡、コンタクトとお別れ | |
| 9.10 | ミスター・パートナー No156 | 127 | 奥山 | たった30秒で視力が回復 | |
| 8. 1 | 月刊FLIX | ビジネス社 | 115 | 奥山 | 目と映画 |
| 7. 6 | 月刊ホスピタウン | 36 | 奥山 | 近視を矯正する より安全・低侵襲に術式はさらに進化 |
|
| 6. 1 | 月刊FLIX | ビジネス社 | 47 | 奥山 | 目と映画 |
| 4. 1 | 月刊 エアステージ | イカロス出版 | 130 | 奥山 | キャビンクルー志望者のための メディカルクリニック |
| 3. 1 | 月刊スキージャーナル | スキージャーナル(株) | PR | 奥山 | 新手術「PRK」で切らずに視力を回復! |
| 1. 5 | 尖端 NEWS LETTER Vol3 No3 | 先端医療技術開発研究会 | 7 | 奥山 | 高齢者の目の病気と視力回復 |
2000年10月11日
PRKで本当に視力は戻るのか(日刊ゲンダイ 2000年10月11日号)
日刊ゲンダイ 2000年 10月 11日号
PRKで本当に視力は戻るのか
 近視矯正手術が話題になっている。簡単な手術で不便なメガネやコンタクトからおさらばできるというのだから、近視に悩む人にとって、こんな朗報はない。手術が初めて紹介された17年ほど前、日本中に一大センセーションが巻き起こったのも当然のことだろう。
近視矯正手術が話題になっている。簡単な手術で不便なメガネやコンタクトからおさらばできるというのだから、近視に悩む人にとって、こんな朗報はない。手術が初めて紹介された17年ほど前、日本中に一大センセーションが巻き起こったのも当然のことだろう。
しかし、「近視矯正手術は危ないのでは」という漠然とした不安がいつまでもあるのも事実。屈折力を変えるため手術は目の角膜にメスで傷をつけたり、レーザーで角膜を照射したりする。視力を戻すためとはいえ角膜をあえて傷つけるのだから、万一失明したらと考えるのも無理はない。
 これまで多くの近視矯正手術を手掛けてきた参宮橋アイクリニック五反田院長・奥山公道医学博士はいう。
これまで多くの近視矯正手術を手掛けてきた参宮橋アイクリニック五反田院長・奥山公道医学博士はいう。
「技術は進歩していますし、近視矯正手術はこれからは身近になり、常識になるでしょう」
奥山院長はロシアのフイヨドロフ博士によりRK手術を受けた最初の日本人だ。当時内科医だった奥山院長は自らの体験から眼科医となり、以来17年間わが国で矯正手術を手掛け、1万例以上の実績を持つ治療のパイオニアである。最初のころはダイヤモンドメスを用いたRK手術。レーザーメスによるPRK手術を実施していたが、どうしても目を切ることに抵抗を感じ、「切らずに治す」ことはできないかと研究・開発したのが独自のPRKという方法だった。
「従来のPRKはレーザーメスで角膜の表面の中央を一部除去し平面化させ近視を改善するものでした。だが機種によって角膜表面に幾何学的に模様が残ることがあったのです。また、最近注目されているLASIKはカンナのようなもので角膜をはがすように切る。その刃が鈍い場合、振動で微妙なうねりが発生するケースもあり、後に乱視になることもあるのです」(前出・奥山院長)
そこで奥山院長が開発したのが、メスやカンナによる除去作業はいっさい行わず、目に触れず最初からレーザーのみを使う方法。これが最大の特徴。患者はレーザー光源を30秒前後擬視しているだけでいいのだ。
レーザー光源を30秒前後凝視するだけ・・・
「目に特別なメスやカンナを入れるとなると恐怖感がある。ところが、私の手術は目に触れずに進め安心感を与えることができるのです。この方法はレーザーの照射を微調整しながら角膜の表面を蒸発させ、コンタクトレンズ状にします。これで屈折力を変え焦点を合わせることができるのです。結果、0.03が0.7、0.07が1.0といった具合に93%以上の確率で患者さんの希望する視力に矯正することが可能です」
しかし、PRKにデメリットがないわけではない。角膜表面の治癒に2-3日を要し、術後の痛みが1-2日間ある。視力の安定に1-3カ月かかるので、忙しい人は一考を要する。白内障、緑内障といった目の病気を持
つ人は手術不可。また、保険適用外で片目だけでもおおよそ30万円と高額だ。
米国では近視手術を受けている人が年間34万人以上。海の向こうでは近視矯正手術は常識になりつつあるのだ。近視大国のニッポン。近視は切実な問題でもある。
ここはじっくり考えて判断したい。
●問い合わせ=参宮橋アイクリニック
03-3411-0005
2000年5月3日
2000年度分
| 日付 | 雑誌・新聞名 | 会社 | ページ | 執筆 | 内容 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.16 | PRESIDENT | 176 | 近視手術最前線を行く | ||
| 10.11 | 日刊ゲンダイ | 8 | 奥山 | レーザー照射だけのPRKで 本当に視力は戻るのか |
|
| 9.29 | 週刊金曜日 | 週刊金曜日 | 52 | 参宮橋アイクリニック | 近視手術体験記 さよならメガネ&コンタクト? ちょっとピンぼけ裸眼視力1.2 |
| 6. 2 | 週刊金曜日 | 週刊金曜日 | 26 | 参宮橋アイクリニック | 近視手術体験記 さよならメガネ&コンタクト 私の顔からメガネが消えた |
| 6. | 国際グラフ | 国際グラフ | 112 | 奥山 | 30秒間光源を見るだけの近視手術 |
| 4.21 | 週刊金曜日 | 週刊金曜日 | 34 | 参宮橋アイクリニック | 近視手術体験記 さよならメガネ&コンタクト たった30秒で切らずに治す |
| 3.24 | 週刊金曜日 | 週刊金曜日 | 34 | 参宮橋アイクリニック | 近視手術体験記 さよならメガネ&コンタクト? 近視0.03を治そうと思った理由 |
| 2. 26 | 毎日新聞 | 厚生省 奥山 | 近視手術やっと国がお墨付き |
2000年4月2日
Ophthalmosurgery
A.D. Semyonov, A.V. Doga, G.F. Kachalina, K. Okuyama,
I.A. Alisov, V.S. Tyurin, V.A. Sugrobov, A.G. Evsyukov
 Photoastigmatic Refractive Keratectomy
Photoastigmatic Refractive Keratectomy
with the“Profil-500”for Correction
of Compound Myopic Astigmatism
The paper analyses clinical and functional results of the transepithelial PARK with the excimerlaser device “Profi1-500″ performed in 250 eyes of 131 patients between the ages of 18 and 45 with compound myopic astigmatism to 5.0 D and myopia to 10.0D.The follow-up was 3years. In 90% of cases visual acuity of 0.5-1.0 without correction or with weak myopic correction not more than -2.0D was achieved by the operation. Complete correction of astigmatism was obtained in 74% of cases, residual astigmatism from -0.5 to -0.75D(physiological) was found in 22.8% of cases, from -1.0 to -1.5D in only 3.2% of cases and only in eyes with initial astigmatism of 4.0-5.0 D. The refractive result agreed with the calculated data in 96.1% of cases.
The method of excimerlaser correction of compound myopic astigmatism,i.e.,Photo astigmatic refractive keratectomy(PARK),acquires the growing popularity among eye surgeons in Russia and worldwide.
However most specialists dealing with this problem and using different excimer laser devices agree that the most accurate and predicted result is achieved in spherical rather than in cylindric refraction component. From literature, PARK decreases spherical refraction component by 75-95%, on average, and cylindric one by 47-81%. After operation, the best visual functions are recorded, as a rule, in correction of astigmatism to 2.0 D with myopia to 6.0 D [2-9].
It’s should be stressed that from 1986 workers of the Center of Laser Surgery at the Svyatoslav Fyodorov SI IRTC “Eye microsurgery” have pioneer inventions of several generations of ophthalmic laser devices “Profil”.
In 1995 the forming optical system of “Profil-400″ which worked on the basis of absorptive gas cell was modified. “Profil-500″ contains basically new laser system* which was created in cooperation with the Center of Physics lnstrument-making at the Institute of General Physics of Russian Academy of Sciences headed by the Nobel Prize winner A.M. Prokhorov. This device allows simultaneous correction of not only myopia of any value [1] but correction of compound myopic astigmatism due to formation of ellipsoid profile of laser ray distribution with the set spatial configuration and selective reprofiling of the corneal surface.
The objective of the study is the analysis of clinical and functional results of PARK in correction of compound myopic astigmatism with the “Profil-500″ with the follow-up of 3 years.
* Patent of RF, 24.06.98
 Material and methods
Material and methods
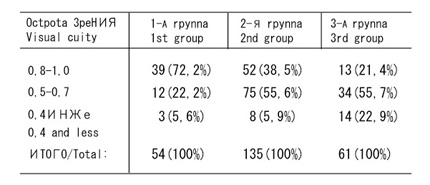
Preoperatively, we examined 250 eyes of 131 patients between the ages of 18 and 45 with compound myopic astigmatism to 5.0 D and myopia to 10.0 D. The first group comprised 54(21.6%) eyes with initial astigmatism to -1.5 D, the second 135 (54.1%) eyes with astigmatism from -1.75 to -3.0 D (Fig. 1), the third 61(24.3%) eyes with astigmatism from -3.25 D to -5.0 D.
Direct astigmatism was foundiin 185(74%) eyes and reverse one in 65(26%) eyes. Spherical refraction component to 3.0 D was recorded in 31(12.4%) eyes, from 3.25 to6.0 D in 137(54.8%), and from 6.25 to 10.0 D in 82(32.8%) eyes.
Visual acuity without correction exceeded 0.05 in none of the cases. Visual acuity with maximal glass correction was 0.1-0.2 in 7 (2.8%) eyes, 0.3-0.4 in 33(13.2%) eyes, 0.5-0.7 in 139 (55.6%), and 0.8-1.0 in 71 (28.4%) eyes. Thus, corrected visual acuity of 0.5-1.0 was recorded in 210 (84%) eyes preoperatively. The similar retinal visual acuity was. in 235 (94%) eyes.
In all cases PARK was performed by transepithelial method, i.e., with subsequent evaporation of epithelium, Bowman’s membrane, and superficial layers of the corneal stroma. Refraction effect was calculated using software elaborated at the Center of Laser Surgery of the SI IRTC “Eye microsurgery” in Windows system.
The operation lasted not more than 1.5 min without any intraoperative complications.
 Results and discussion
Results and discussion
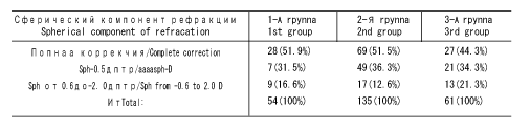
Complete correction of astigmatism by 6-l2 months and more after PARK was recorded in 48 (89.2%) eyes from the 1st group, in 98 (72.6%) from the 2nd group, and in 39 (63.9%) eyes from the 3rd group.
Residual astigmatism in groups at the same time postoperatively was the following: in the 1st group astigmatism to -0.5 D was found in 6(10.8%) eyes; in the 2nd group astigmatism to -0.5 D was recorded in 22 (16.3%) eyes (Fig. 2), -0.75 D in 15 (11.1%) eyes, in the 3rd group astigmatism to -0.5 D was found in 6 (9.8%) eyes, -0.75 D in 8 (13.2%), -1.0 D in 5 (8.2%) and -1.5 D in 3 (4.9%) eyes. Data are presented in Table 1.
Thus, from the total number of eyes operated on, by 6-12 months after PARK full correction of astigmatism was diagnosed in 185 (74%) eyes, residual astigmatism -0.5 and -0.75 D, regarded as physiological, in 57 (22.8%) eyes, from -1.0 to -1.5D in only 8 (3.2%) eyes from the third group with the high initial astigmatism. In none of the cases astigmatism exceeded -1.5 D.
In 65 eyes with residual astigmatism from -0.5 to -1.5 D, its axis remained stable in 35 (14%) eyes and changed within 5-10゚ in 30 (12%) eyes. In none of the cases deviation of the residual astigmatism axis exceeded 10゚.
From the total number of eyes operated on complete correction of the spherical component of refraction was achieved in 124 (49.6%) eyes, residual sphere -0.5 D in 87 (34.8%) eyes, sphere from -0.6 to 2.0 D in 39 (15.6%) eyes. Notably, weak myopic refraction found 6 months – 3 years postoperatively coincided with the calculated, i.e., planned, one in 96.1% of cases. Such “planned undercorrection” was related to the age of patients, their social demands and refraction of the fellow eyes. In none of the cases undercorrection was more than -2.0 D (Table2).
Hypercorrection up to +0.25 D from emmetropia, which did not affect postoperative visual acuity, was found in only 3 eyes 6-l2 months after PARK and only using refractometry in conditions of cycloplegia (1.2% of cases). It’s should be noted that 1.5-2 years postoperatively, hypercorrection was not already found in these eyes.
By 6-l2 months postoperatively and during the whole follow-up, visual acuity 0.5-I.0 without correction or with weak myopic predicted correction was achieved in 94.4% of cases in the 1st group, in 94% in the 2nd, and in 77% of cases in the 3rd group. On the whole, there are 225 (90%) eyes as compared to 210 (84%) eyes with the same visual acuity in glasses preoperatively (Table 3).

The correspondence of this visual acuity to the analogous retinal one was recorded in 95.7% of cases. It is because of the fact that postoperatively, we found increase of visual actlity in 30 eyes by 0.1-0.2 as compared to the analogous visual acuity with glass correction preoperatively.
Dynamics study showed that the corneal refraction, according to the data of ophthalmometry, by 6-12 months postoperatively and during the whole follow-up to 3 yearswas 37.59 ± 0.72 D, on average. Thickness of the corneain the centerwas not less than 300 um in any case that showed correct choice of individual ablation
reglmen.
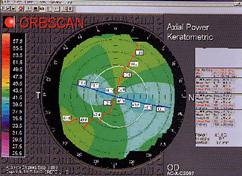
Clinical and functional results of the study are confirmed by the data of keratotopographical examinations indicating the following things: achievement of the smooth ablation profile of the cornea with the maximal refractive effect in the central zone and gradual change of the corneal refraction in the each point of the cornea along the entire zone of the excimer laser influence in all cases; symmetrical flattening of the cornea along the axis which has had the greatest refraction preoperatively; multifocali-zones with smooth over fall of refraction from 1.0 to 3.0 D without sharp intermediate zones both inside each zone and between them, along the whole zone of influence; absence of defects in keratotopographic images such as “crescent”, “key-hole”, and “central islets”; rear decentrations of ablation zone with regard to the center of the pupil and the cornea not greater than 0.75 mm and 0.18-0.32 mm, on average.
The above data of keratotopography which was performed at different terms after transepithelial PARK using “Profil-500″ explain the fact that most patient did not complain of negative subjective feelings as lights, crepe, dazzling, and halos and, besides, many of them did not use glasses for the work at near distance [1].
Thus, the results obtained show that the developed technology of transepithelial PARK using “Profil-500″ is safe, highly effective and predictable refractive excimer laser interference which allows simultaneous complete correction of myopia and compound myopic astigmatism of different degree.
